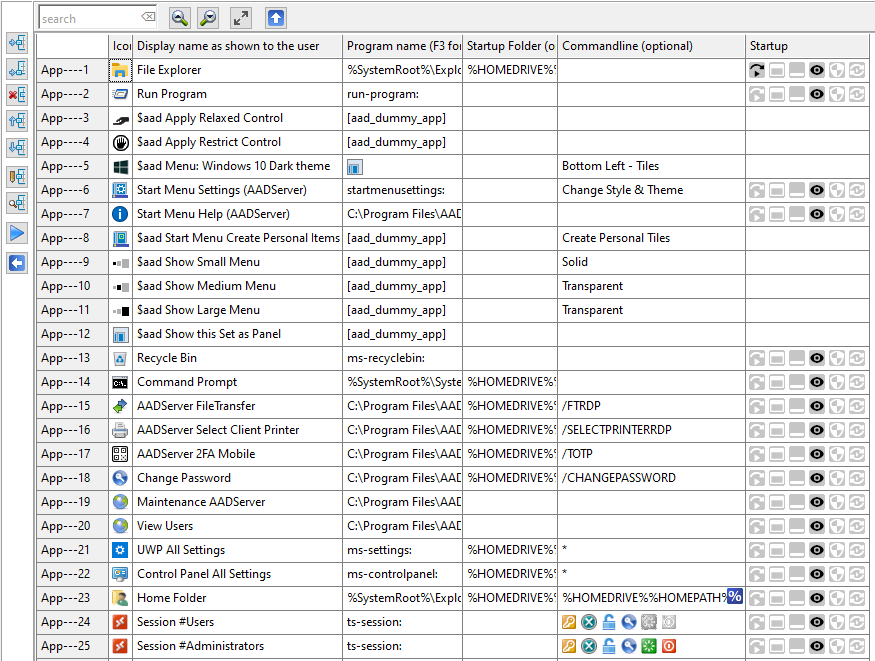
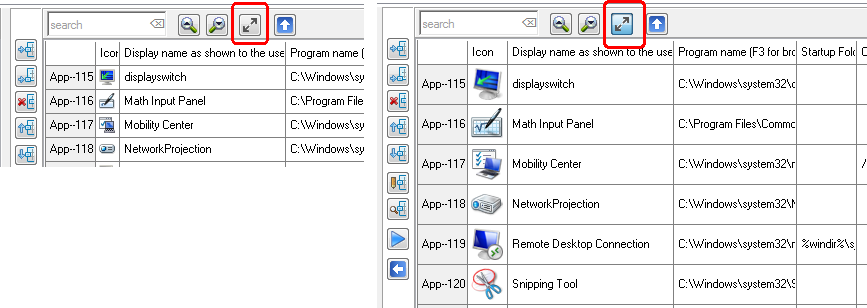
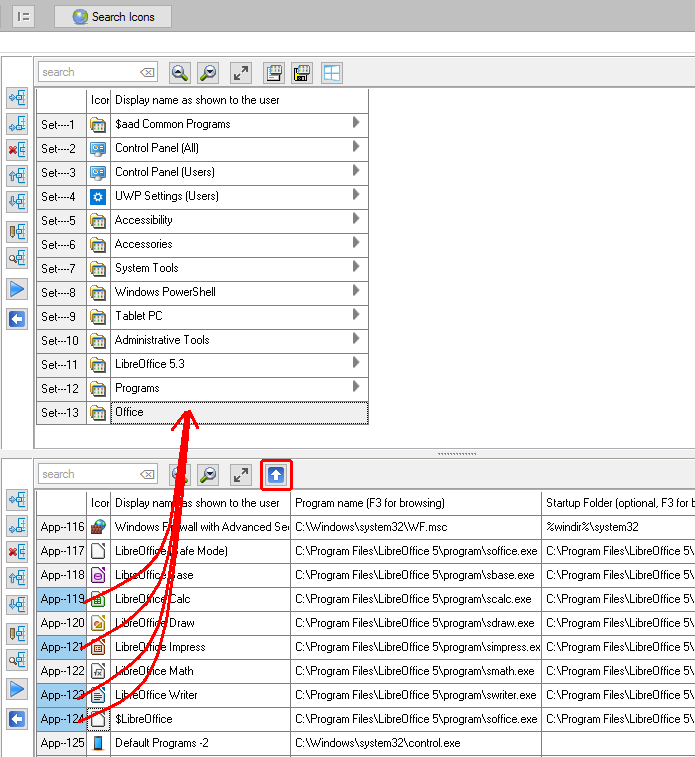
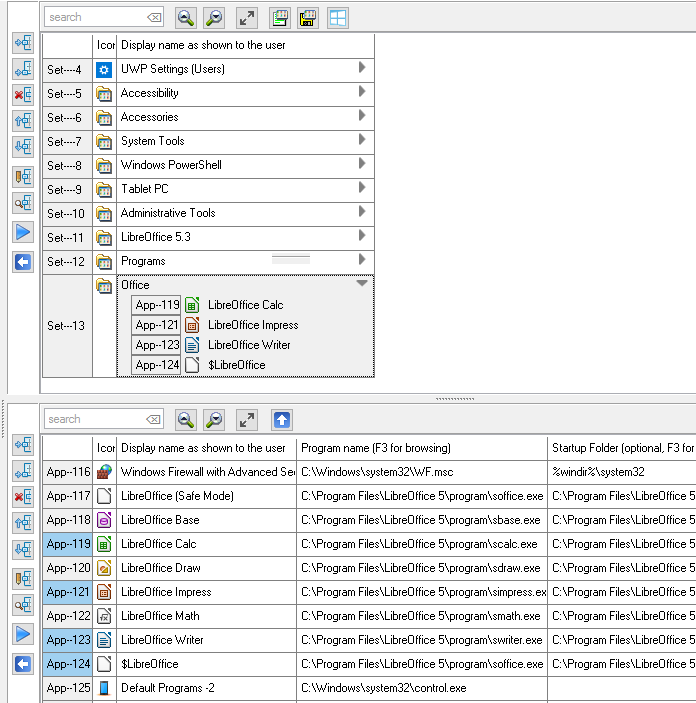
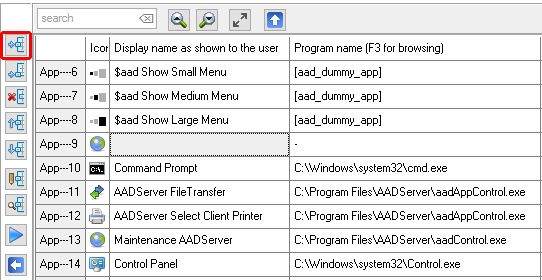
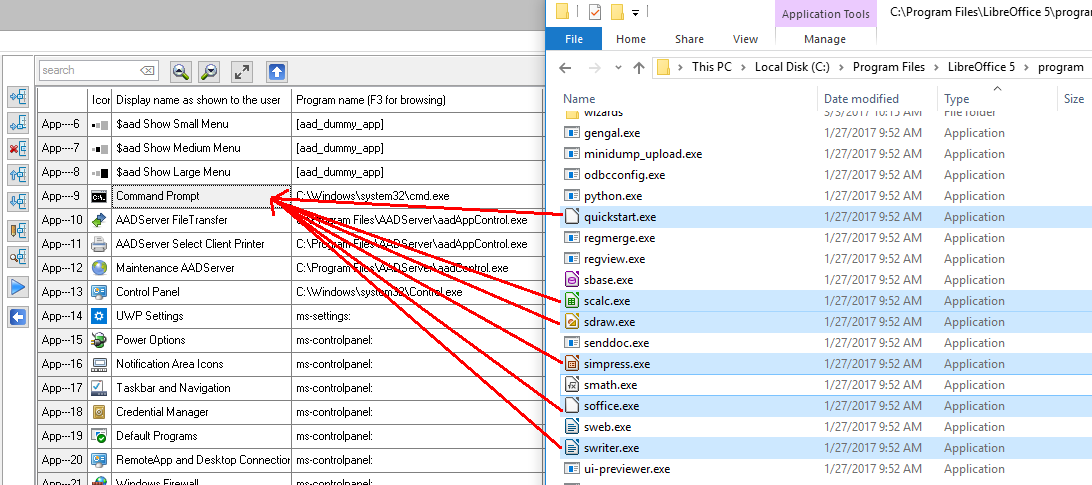

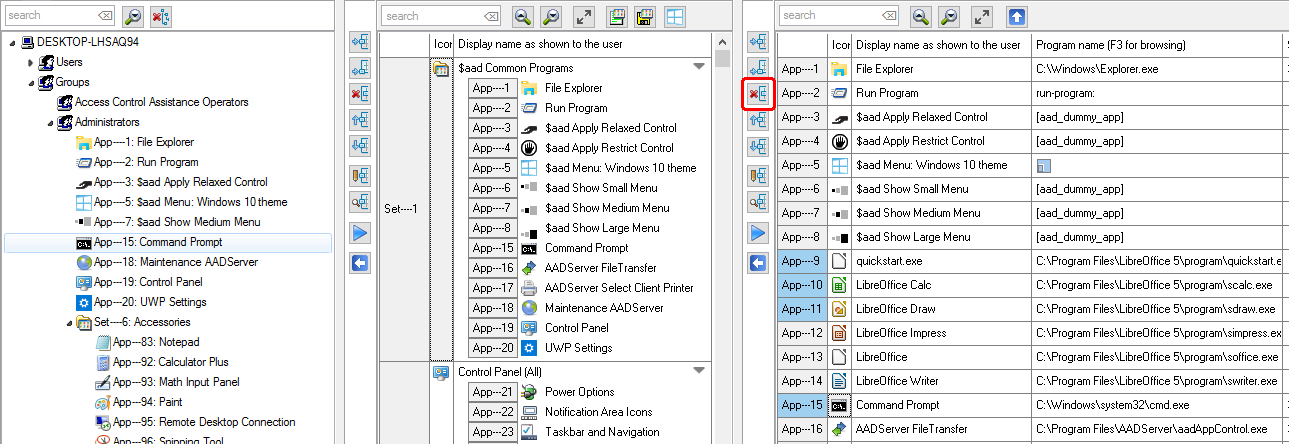
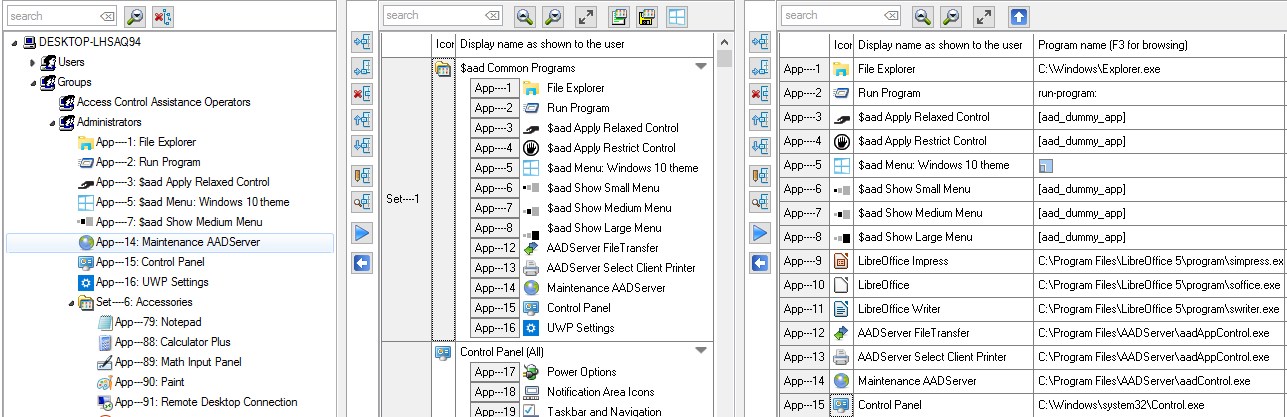
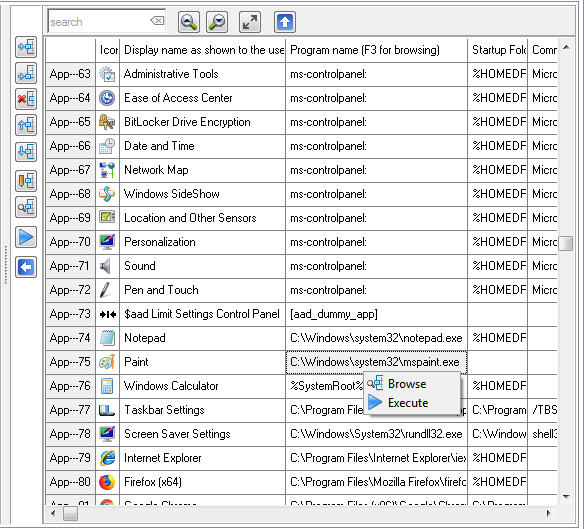
Sorting Applications is relevant, because the Sort Order as shown here, will be the same order as the Applications do appear in the Start Menu of the User. The User can not sort the Applications as they are shown in the Start Menu.
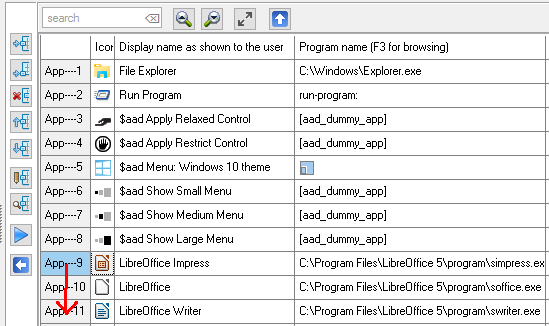
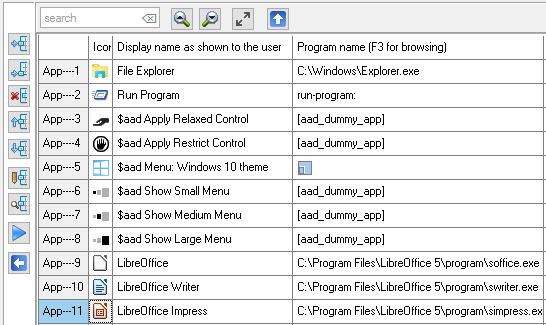
Applications do have 6 properties
When no custom Icon is assigned to the Application, the default Icon of the Application will be shown and used in the Start Menu of the user.
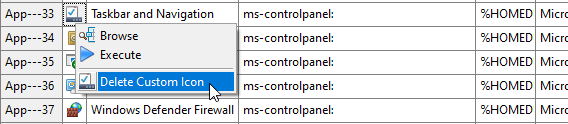
Deleting the Icon implies that the custom Icon will not be used anymore, and that the default Icon of the application will be shown and used in the Start Menu of the user.
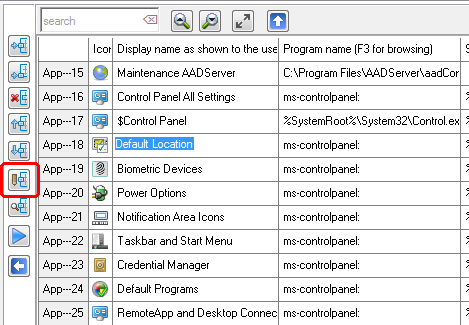
When a Display Name starts with $, the Program is "Hidden" and will not appear in the Start Menu of the User. However, the User is allowed to use the program; the User can use the program.
When Restricted Application Control is applied, the User can only start Applications that are explicitly assigned to the User by the Administrator. However, It might happen that an User needs to be able to use some additional Applications.

Libre Office comes with a TrayIcon-quickstart utility. This Program does not have to appear in the Start Menu of the User, but the User might want to be able to run it and use it. This is where "Hidden" can be used. By defining and assigning a "Hidden" program to an User, the "Hidden" program will not appear in the Start Menu of the User. But the "Hidden" program can be started and used by the User.
In this example the program $quickstart.exe has been set for "AutoStart".
Text behind # is treated as comment and will not appear in the Start Menu of the User.
Example:

The text #Users in App-25 does explain to the Administrator that this Session Menu is for the Users.
The text #Users itself does not appear / is not shown to the Users:
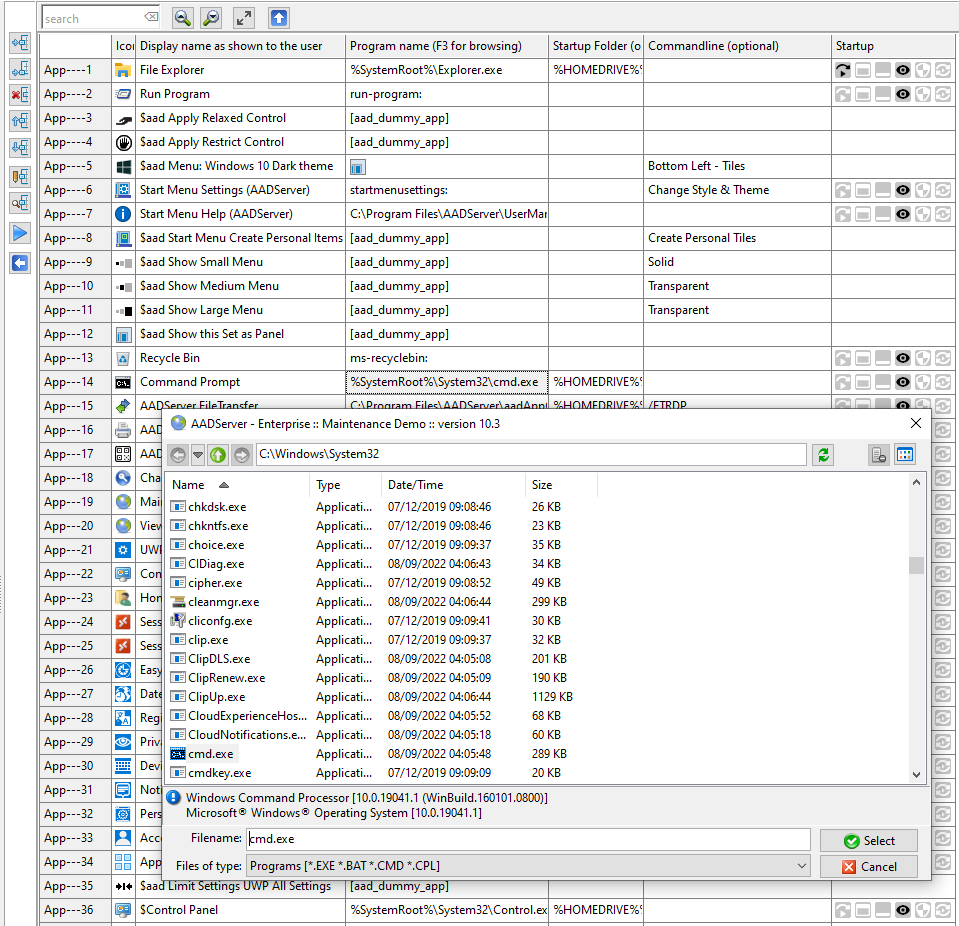
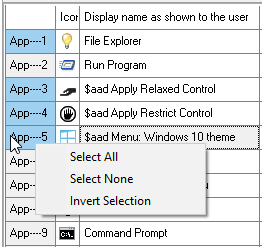
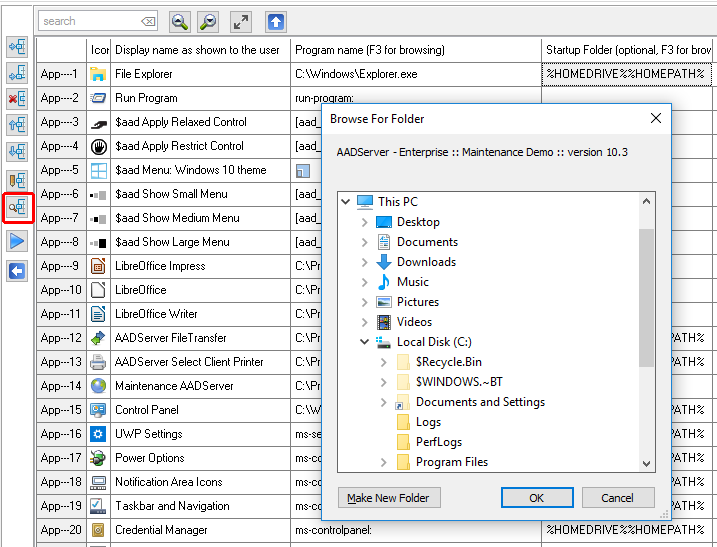
The browse-popup Windows has the option to show checkboxes with each programs. By selecting multiple programs, multiple programs can be added to Application Control in 1 go:
Usually the contents of the Startup Folder depends on the Program.
Usually the contents of the Command Line depends on the Program.
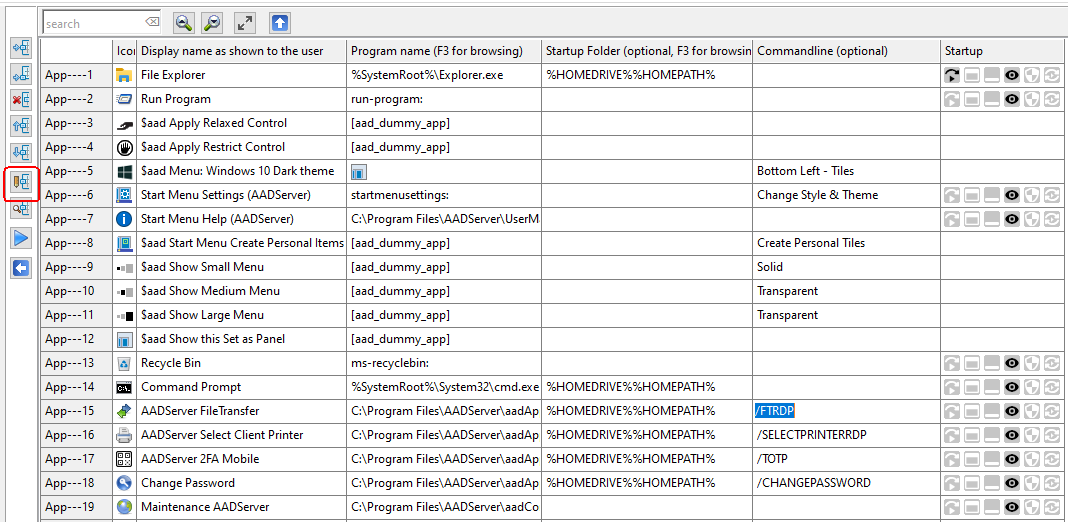
An Application can be started as follows:
 |
Auto‑Start | The Application will be started directly after the login of the user. Multiple Applications can be flagged as Auto‑Start. |
 |
Maximize | When started, the Application will be initially shown Maximized. The user is able to Restore or Minimize the Application. |
 |
Minimize | When started, the Application will be initially shown Minimized. The user is able to Restore or Minimize the Application. |
 |
Visible | Default all Applications are shown Visible. The User can interact with the Application. An Application can be flagged as "not shown Visible" or "Hidden". An user can not interact with a Hidden Application. This option can be useful, for example, for starting CMD-files which will start another Application. In combination with Autorun, you can start some kind of Hidden Service application for the user, without showing it. For instance, you might use it to start some Anti Virus client software without showing it to the user. |
 |
Elevated | The Application will be started "Elevated". |
 |
Auto‑ReStart | When the Application is terminated, it will be started again by AADS. Multiple Applications can be flagged as Auto‑ReStart. |
In the example below, the Administrator has created an 2th CMD-App that is marked for Elevation:
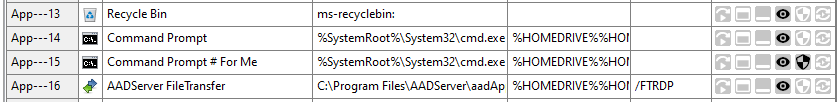
When it is started, one can expect the following:
Environment variables can be used in:
Example:
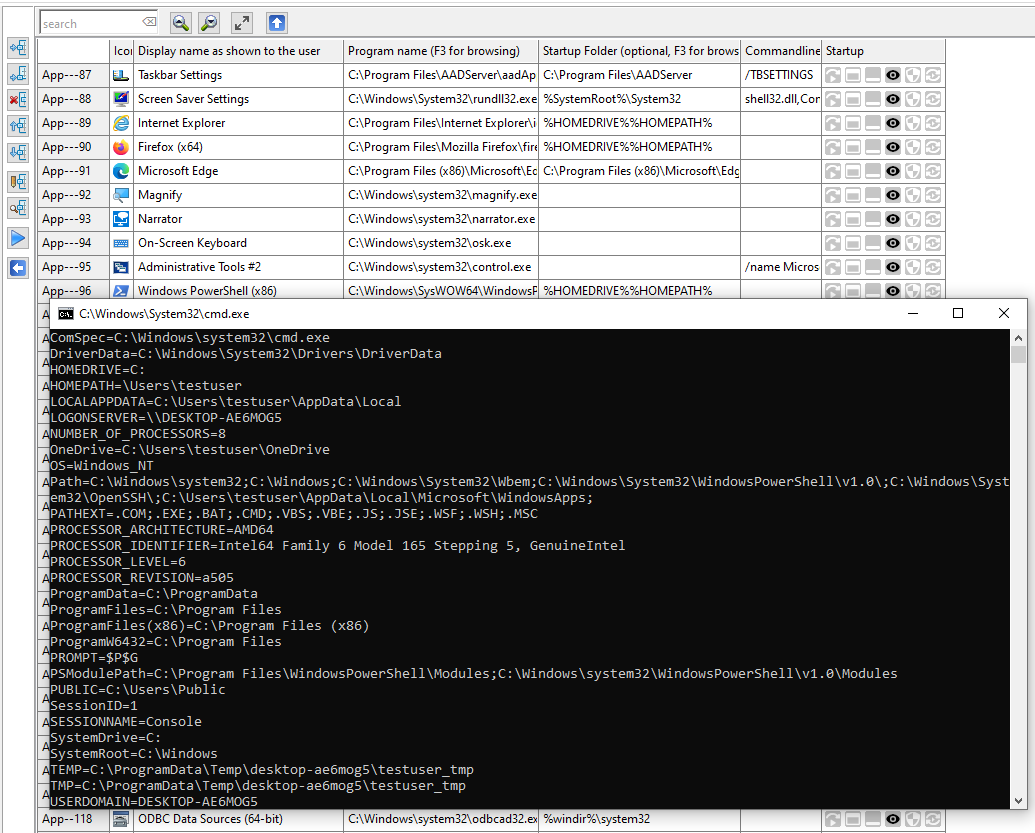
The Administrator can open a DosBox, using the command Set, and see all the Environment Variables that do exist.
Those Environment Variables can be used while defining Applications for the Users.
| Result for user domain003 | |
| C:\documents\%username% | C:\documents\domain003 |
| %userprofile%\some folder | C:\Documents and Settings\domain003\some folder |
The & character can be used for special character in the range $01 .. $FF (hexadecimal between 1 and 255).
The & character is used as a so called escape character. Examples:
| Result for user domain003 | |
| C:\documents\&25username&25 | C:\documents\%username% |
| C:\documents\&26username&26 | C:\documents\&username& |
| C:\documents\&22username&22 %username% | C:\documents\"username" domain003 |
| "C:\documents\username" %username% | "C:\documents\username" domain003 |
Take a good look at the last 2 examples: the first occurrence of username is not considered to be an environment variable because it is not enclosed in %. In the third example it is enclosed in &22. This is the hex-value of the character ", so result will be "username".
The second occurrence of username is considered as an environment variable because it is enclosed in %. Therefore it is replaced with domain003 in this example.
The &XX appearance will always be translated to a character:
| Command line parameter or Startup Folder | Result for user domain003 |
| C:\documents\&25username&25 | C:\documents\%username% |
| "C:\documents\&25username&25" | "C:\documents\%username%" |
| "C:\documents\&26username" | "C:\documents\&username" |
|
© 2012-2023 AADS WorldWide. Terminal Server | Application Server | Remote Desktop solutions | Firewall |